Technical Articles
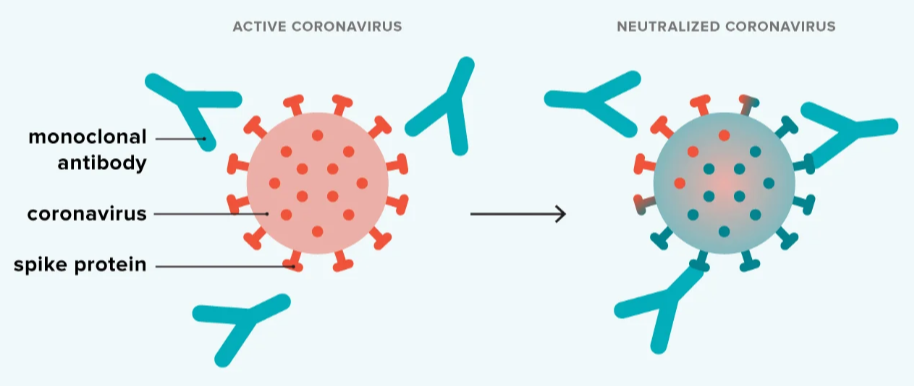
How to Select the Right Monoclonal Antibody Technology
Monoclonal antibody (mAb) technology has Developed by Georges Köhler and César Milstein in 1975, this technology involves producing antibodies from a single clone of B-lymphocytes, ensuring high specificity. Unlike polyclonal antibodies, which recognize multiple epitopes, monoclonal antibodies target a single epitope, making them highly precise tools in medical applications.
T Cell Activation
T cell activation is a crucial process in the immune system, enabling the body to fight infections and diseases. T cells, a type of white blood cell, are activated when their receptors recognize specific antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells. This recognition occurs through the binding of the T cell receptor (TCR) to the antigen-MHC complex on the APC.
From basics to applications: a comprehensive analysis of protein characterization
Proteins are essential macromolecules that play a vital role in nearly all biological processes. They are the building blocks of life and are responsible for the structure, function, and regulation of body tissues and organs. Proteins act as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies, facilitating biochemical reactions, signaling pathways, and immune responses. Their diverse functions make them indispensable for the growth, repair, and maintenance of cells, as well as for overall health and development.
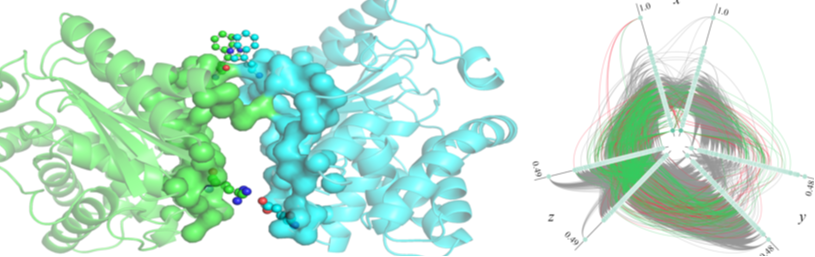
Protein-Protein Interactions
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) refer to the physical contacts established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces. These interactions are important for all biological processes, enabling proteins to form complexes, carry out their functions and regulate various cellular activities.
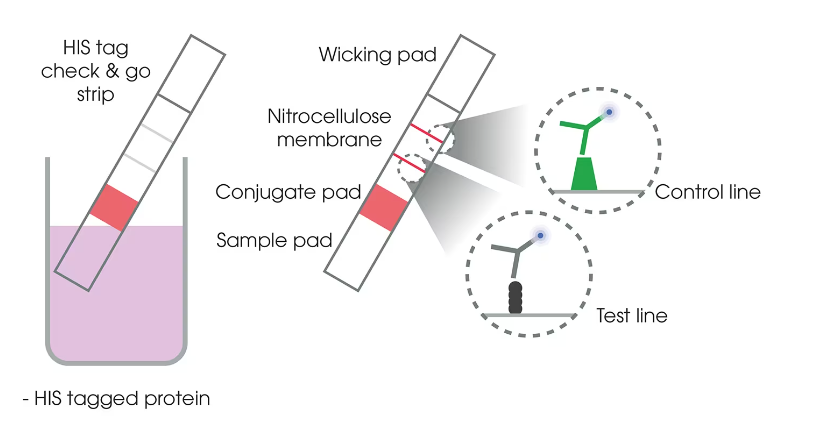
His Tag A Key Tool for Efficient Protein Characterization
The His tag, short for polyhistidine tag, is a sequence of six to ten histidine residues added to proteins to facilitate purification and detection. This tag binds strongly to metal ions like nickel or cobalt, allowing tagged proteins to be isolated using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC). His tags are widely used in biochemical research due to their simplicity, efficiency, and minimal impact on protein function. They enable researchers to purify proteins from complex mixtures, study protein-protein interactions, and perform structural analyses.
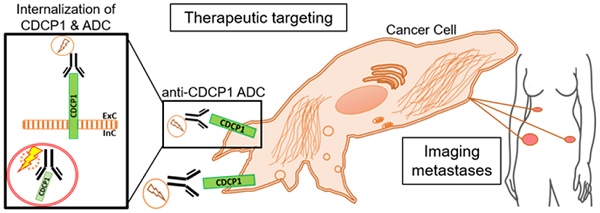
Unveiling CDCP1 Its Role in Tumor Invasion and Metastasis
CDCP1 (CUB domain-containing protein 1), also known as CD318, SIMA135, gp140, or TRASK, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein. It is prominently expressed in various stem and precursor cells, including hematopoietic stem cells and neural progenitor cells. CDCP1 plays a crucial role in processes such as cell adhesion, migration, and survival.
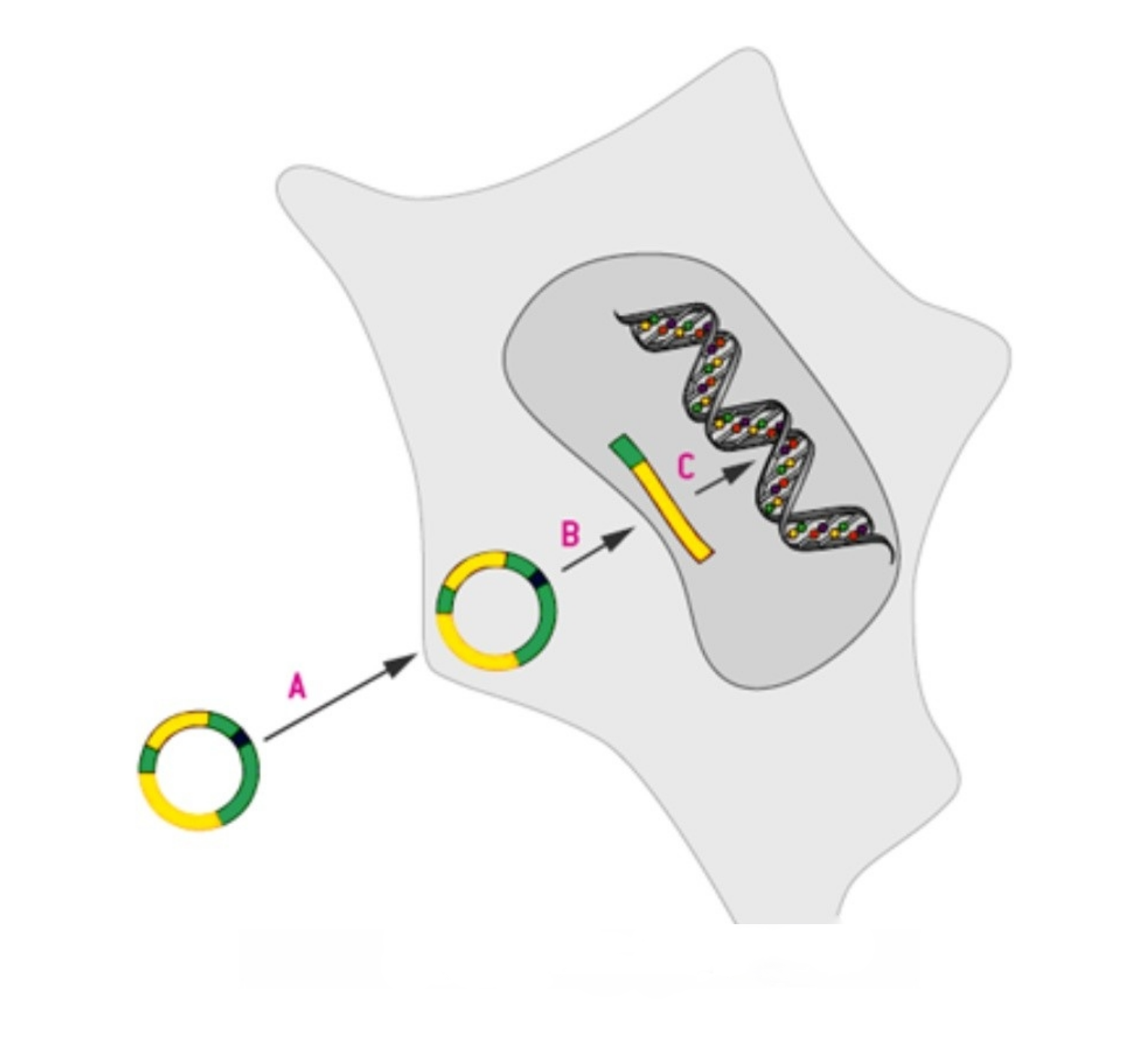
Application and research prospects of stable cell lines
A stable cell line is a population of cells that maintain consistent characteristics over many generations. These cells are genetically modified to express or silence specific genes, allowing researchers to study gene function, drug effects, or disease mechanisms. By remaining stable over time, they provide reliable and reproducible data for various scientific experiments.